As many fleets in the long-haul transportation sector know, Transport Canada’s ELD Mandate is quickly approaching and will require countless vehicle-based businesses to transition to electronic logging devices (ELDs). As there will be penalties for fleets who do not use these devices, fleets are forced to update their paper logbooks. While there is basic training related to how to properly use ELDs, fleet managers must also become familiar with additional ELD information to properly abide to hours-of-service (HOS) regulations.
Widely Known Benefits Of ELDs
When electronic logging devices are purchased and implemented, many fleets are made aware of basic benefits. Before the mandate, it is important to review the benefits and ensure you are aware of how to see the results. Typically, fleets can see:
- Accurate logging for HOS as ELDs read the odometer and monitor the engine to collect various data to make sure drivers and managers abide by the Federal Motor Carrier Safety Administration (FMCSA) regulations
- Prevention of driver fatigue since drivers won’t be overworking – accurate logs will ensure drivers are not over-driving
- Increased public safety as a result of decreased driver fatigue and overworking
- Improved data collection when investigating driving incidents as officials can use information gathered from the ELDs to rule out theories to why a driving event occurred
- Reduced tampering of company tools or devices as the ELDs approved by the FMCSA are tamper proof and automatically display HOS
Additional Information About ELDs That Fleets Can’t Go Without
While the above information is great, the Transportation Compliance Specialists at GoFleet have concluded that there is more to know. Without knowing such information, fleets may run into issues or continue to miss out on fully leveraging their devices. As a result, we believe the following is critical to know:
- Fraudulent changes to logs are actively stopped as FMCSA regulations limit what edits can be done (even with fleet manager access) – in addition, logs cannot be switched between drivers.
- Crossing the border will require drivers to adjust their device to display the country they are in. This will allow the ELD to automatically update to follow the regulatory frameworks of the country that they are in. Drivers are still recommended to review the regulations of the country they are about to enter, before crossing the border, so that they are not caught off guard.
- Even though the chances that the ELD will fail are low, drivers are allowed to revert back to paper logging if the ELD malfunctions. In case the ELD does fail, they can easily prove to officers that the tablet malfunctioned and the data was unable to transfer.
- Tampering with the device is easily detectible as ELDs do not only record HOS but whether the vehicle is in movement or not.
- Electronic logging devices must be accredited by a 3rd party certification body who is certified under the FMCSA – self certification is not allowed.
Properly Educating Drivers About The Mandate
It is not enough to only have fleet managers knowledgably about the incoming ELD mandates. Fleet drivers must be properly trained in everything that we have discussed.
From the standard operating procedures of using the electronic logging device to being aware of how devices are pre-designed to reduce improper utilization, drivers must undergo proper training. It is therefore mission-critical for training courses to be created and assigned in a timely manner for drivers, so that they can be acquainted with the mandates that are being enforced.
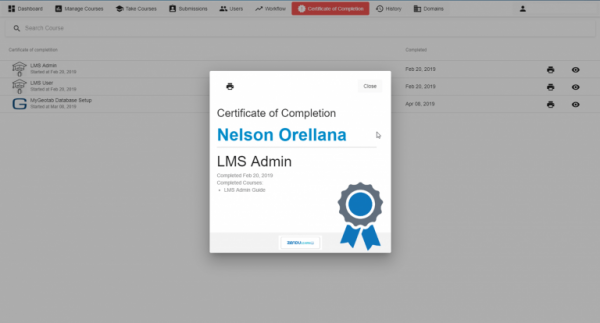
To assist with this, ZenduLearn is the perfect application that can help create, deploy, and track personalized learning and training.
With the ELD Mandate approaching in a matter of months, Canadian fleets must prepare and train their drivers. To learn more about how your vehicle-based business can further prepare for the incoming mandate, contact us today to speak with one of our Transportation Compliance Specialists.